
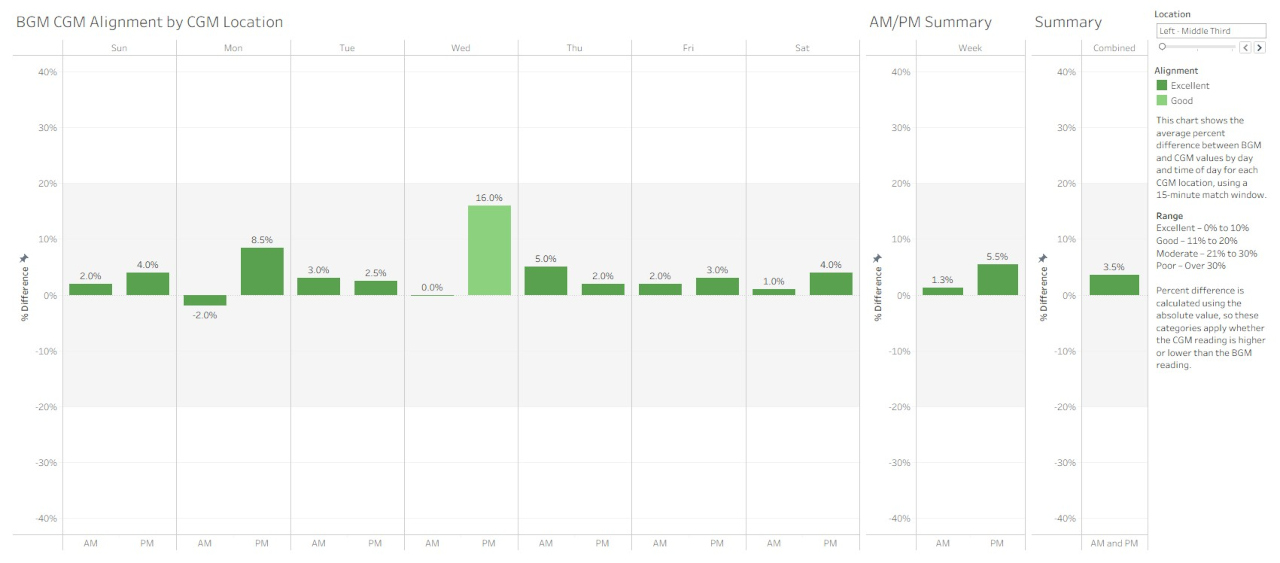
A look at how closely my CGM readings reflect actual blood glucose—and what that reveals about sensor placement and performance.
Abstract
Explore how well continuous glucose monitor (CGM) readings align with blood glucose meter (BGM) results, using real-world data and a 15-minute pairing window. By tracking percent differences and visualizing trends, it becomes easier to evaluate sensor placement, detect performance issues, and make more confident decisions.
Key Points

Researchers have found blood-based epigenetic markers that may help predict heart disease risk in type 2 diabetes, offering a potential path to more personalized prevention and care.
Abstract
An international research team led by Lund University Diabetes Centre has discovered blood-based epigenetic markers that may help predict which people with type 2 diabetes are at risk of serious cardiovascular events. In a study of 752 newly diagnosed participants followed for just over seven years, a scoring tool based on DNA methylation patterns outperformed standard clinical risk calculators, particularly in ruling out low-risk individuals. While further validation is needed, this approach could lead to a simple blood test that supports more personalized prevention and treatment strategies in type 2 diabetes care.
Key Points
Read more: Epigenetic Clues to Heart Risk in Type 2 Diabetes

Scientists have discovered gut bacterium proteins that may one day complement GLP-1 drugs, helping improve blood sugar control, boost fat burning, and support weight management in type 2 diabetes and obesity.
Abstract
Researchers have identified two proteins, RORDEP1 and RORDEP2, produced by certain strains of the gut bacterium Ruminococcus torques, that influence weight, blood sugar, and bone health. Preclinical studies show they increase GLP-1 and PYY, reduce GIP, boost fat burning, and improve liver insulin sensitivity. Early human trials are underway, exploring their potential as next-generation probiotics or protein-based therapies for type 2 diabetes, obesity, and related conditions.
Key Points
Read more: Could a Gut Bacterium Help Transform Diabetes and Obesity Care?
A plain-language guide to how mRNA works and why it matters for future health care
Abstract
mRNA vaccines work by delivering temporary instructions that help the body produce a harmless protein and build immune protection—without using live viruses or altering DNA. Backed by decades of research, this approach offers a safe, flexible alternative to traditional vaccines. Clear explanations dispel common misconceptions and highlight how mRNA technology could one day support treatments for chronic conditions like type 2 diabetes.
Key Points
Page 2 of 23